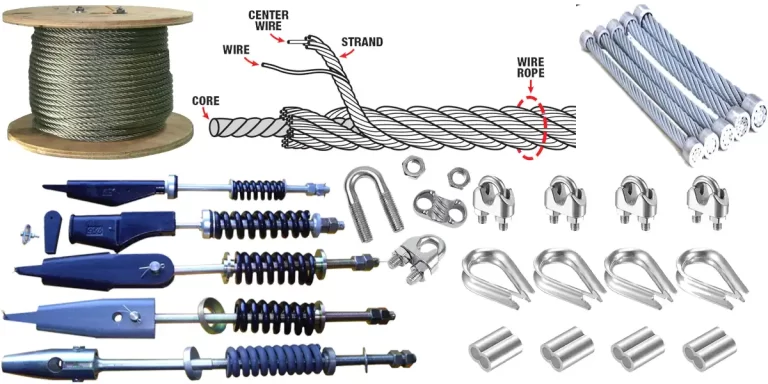
Gulf Tech also sales elevator parts at good price, From commercial elevators to industrial ones, every lift is made up of several different components, each with a unique function, to provide movement and safety in equal measure. Here, we take a closer look at the most important components of an elevator system, highlighting their specific purpose.
The elevator shaft is the space in which the cabin moves up and down when in operation. The size and shape of your elevator shaft will vary, depending on the size and shape of the lift cabin. For instance, elevator shafts are much smaller for passenger carriages but will be much larger for those responsible for carrying heavy goods in factories or warehouses. At the bottom of every elevator shaft, however, is a buffer. A buffer is designed to protect passengers or goods in transit, providing an emergency stop that can halt the descending car through accumulating or dissipating the kinetic energy of the lift car.
The car frame is a steel structure to support lift platform and the door. A safety device is built underneath the frame to instantly grip and stop the elevator if it overspeed’s. It comes with safety gear electrical contacts that cut power supply to halt the fast-moving elevator.
Counterweights are only used for traction elevator applications. A counterweight is an added weight that gives balance to the elevator system and makes it simpler to raise and lower the cab, which reduces the effort required by the lifting machine.
Elevator guide shoes are used to fix the car on the guide rail so that the car can only move up and down [1]. Each elevator car is equipped with four sets of guide shoes, which are respectively set on both sides of the upper beam and under the safety gear seat at the bottom of the car.
The inverter learns the position, and carries out control to accurately stop the elevator at the designated floor position. Simply by selecting the mode in the serial communication option from the upper-level control, it is possible to carry out processes from speed management to creep-less landing control.
A vital component of an elevator or lift system, the speed governor is the regulating system that controls the velocity of the cabin. If for any reason, the elevator begins to surpass the designated speed limit, the speed governor will kick in and reduce the speed accordingly.
Pulleys with large metal cables are used in modern elevators. The cable is wrapped around a groove in the wheel and axle. An electric motor pulls the cable, lifting the car between floors. Several pulleys can be combined to reduce the necessary work to lift a load. One or more deflector sheaves are located between the traction sheave and the elevator car over which the belt is routed to guide the belt to the elevator car. The one or more deflector sheaves include an outer sheave surface having a distance from a sheave axis that varies along a width of the traction sheave.
Pulleys with large metal cables are used in modern elevators. The cable is wrapped around a groove in the wheel and axle. An electric motor pulls the cable, lifting the car between floors. Several pulleys can be combined to reduce the necessary work to lift a load. One or more deflector sheaves are located between the traction sheave and the elevator car over which the belt is routed to guide the belt to the elevator car. The one or more deflector sheaves include an outer sheave surface having a distance from a sheave axis that varies along a width of the traction sheave.
A vitally important mechanical device attached to the elevator, the safety device is crucial in providing protection for passengers and goods in transit. In case of emergency, or if the lift has surpassed its maximum speed limit, the safety device helps maintain a safe and secure ride. we understand the importance of personalized service and the right lifts for your needs. Our team of lift manufacturers in Scotland provide some of the very best services across the country, with expert knowledge, years of experience and unbeatable customer service. If you’re stuck with a problem with your lifts, we have a solution to help. Contact us today!